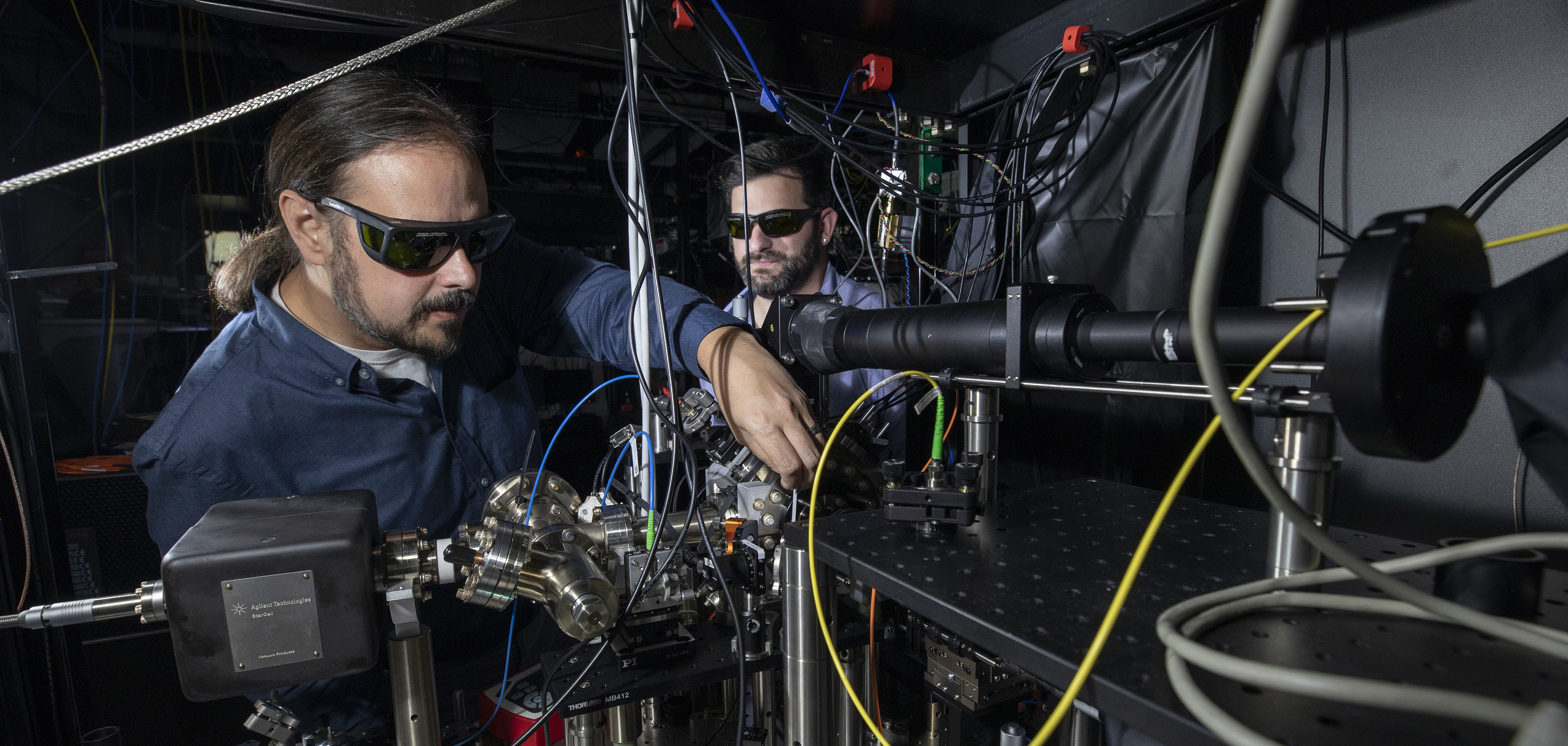
A research team led by the Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) was recently selected for second-phase funding of a $9.2 million project aimed at demonstrating a hybrid computing system that will combine the advantages of classical computing with those of quantum computing to tackle some of the world’s most difficult optimization problems.
Over the next two years, the team plans to use several hundred quantum bits (qubits) made of trapped ions to put the unique capabilities of quantum computing systems to work on these challenges. The team, which also includes researchers from Georgia Tech’s School of Industrial and Systems Engineering, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has already demonstrated key elements of the system using a 10-qubit ion chain.
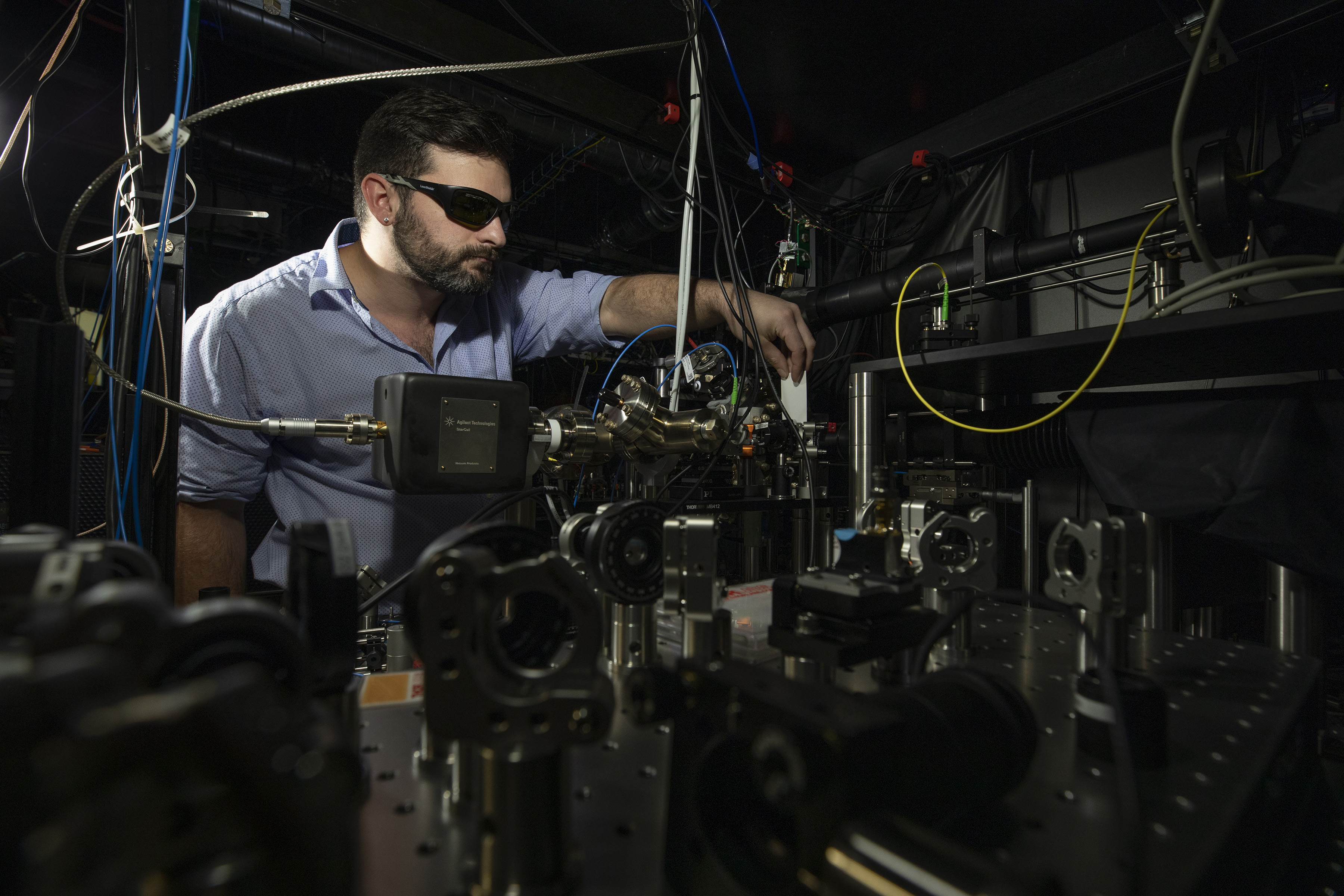

“The implications of a quantum solution to this optimization challenge could be dramatic,” said Creston Herold, a GTRI senior research scientist who is principal investigator for the program, which is known as Optimization with Trapped Ion Qubits (OPTIQ). “Previously intractable problems could be solvable, and computation time could be reduced from days to hours or minutes. That could allow optimization to be applied to many more tasks, improving operational efficiency, and saving time, money, and energy.”
The research is supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) as part of its Optimization with Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum Devices (ONISQ) program. Specifically, the GTRI-led team will use the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) to tackle a difficult optimization challenge known as Max-Cut and related optimization problems.
Optimization Key to Defense and Commercial Applications
Optimization is important to a broad range of defense and commercial challenges, including logistics management, security, reliability, sensing, communications, electronic design and manufacturing, and image segmentation. Package delivery services use optimization algorithms every day to determine the best delivery routes, but some optimization issues are so complex that they cannot be solved using existing approaches. For those, quantum approaches may provide the only solution.
For the quantum component of the project, the research team plans to leverage the massively parallel operations possible with trapped ions, performing many two-qubit gates simultaneously and scaling up to hundreds of qubits. The operations will be performed in two-dimensional ion crystals within Penning traps, devices that contain and control the ions using both a homogeneous axial magnetic field and an inhomogeneous quadrupole electric field.
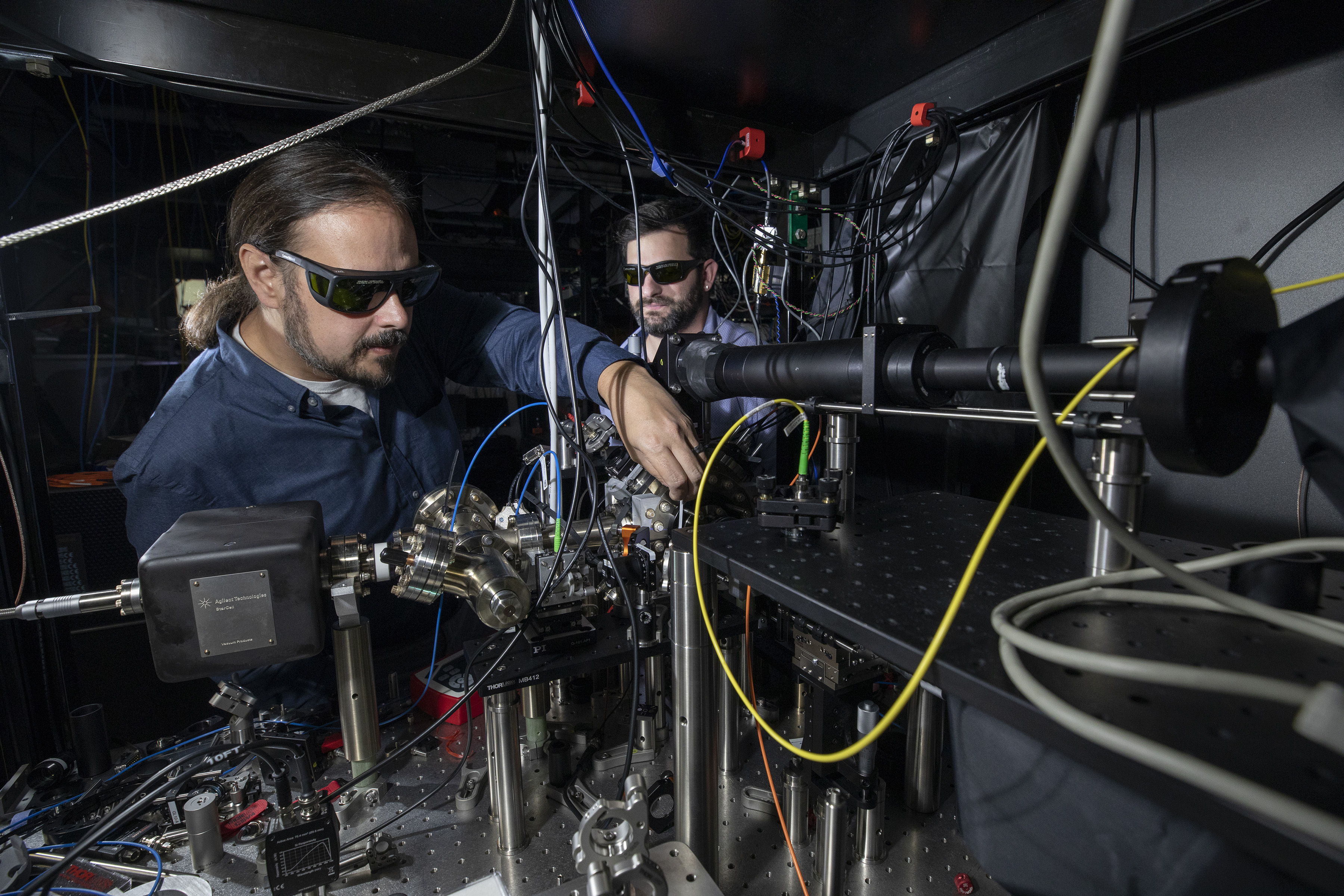

The project will utilize a unique Penning trap configuration that uses powerful rare-earth permanent magnets instead of bulky, cryo-cooled superconducting magnets. GTRI Senior Research Scientist Brian Sawyer and Research Scientist Brian McMahon developed the trapping system, which was part of McMahon’s Ph.D. thesis at Georgia Tech’s School of Physics.
Hybrid Quantum and Classical Computing Approaches
Because quantum and classical computing rely on dramatically different techniques, they provide different strengths that the project can use in a complementary way, said Swati Gupta, an assistant professor at Georgia Tech’s School of Industrial and Systems Engineering who studies complex optimization issues.
“The building blocks are quite different for classical computing and quantum computing,” Gupta noted. “That is exciting and challenging to understand as we build a bridge between these two regimes.”
In some cases, only approximate solutions can now be produced by classical computing systems – and even those may require long run times.
“The speed of operations is very relevant these days because we need to make decisions every second and every minute,” Gupta said. “The dream is that by using a combination of classical and quantum machines, we will be able to significantly beat what can be done with just classical devices.”
Second Phase Builds on Initial 10-Qubit Work
During the first 18 months of the project, the researchers demonstrated that they can prepare their optimization machine using an ion chain composed of 10 qubits. In the second phase, they will tackle the challenge of scaling that up to the hundreds of qubits – and perhaps as many as a thousand – that will be necessary to run the optimization algorithm using controls developed with the 10-qubit system.
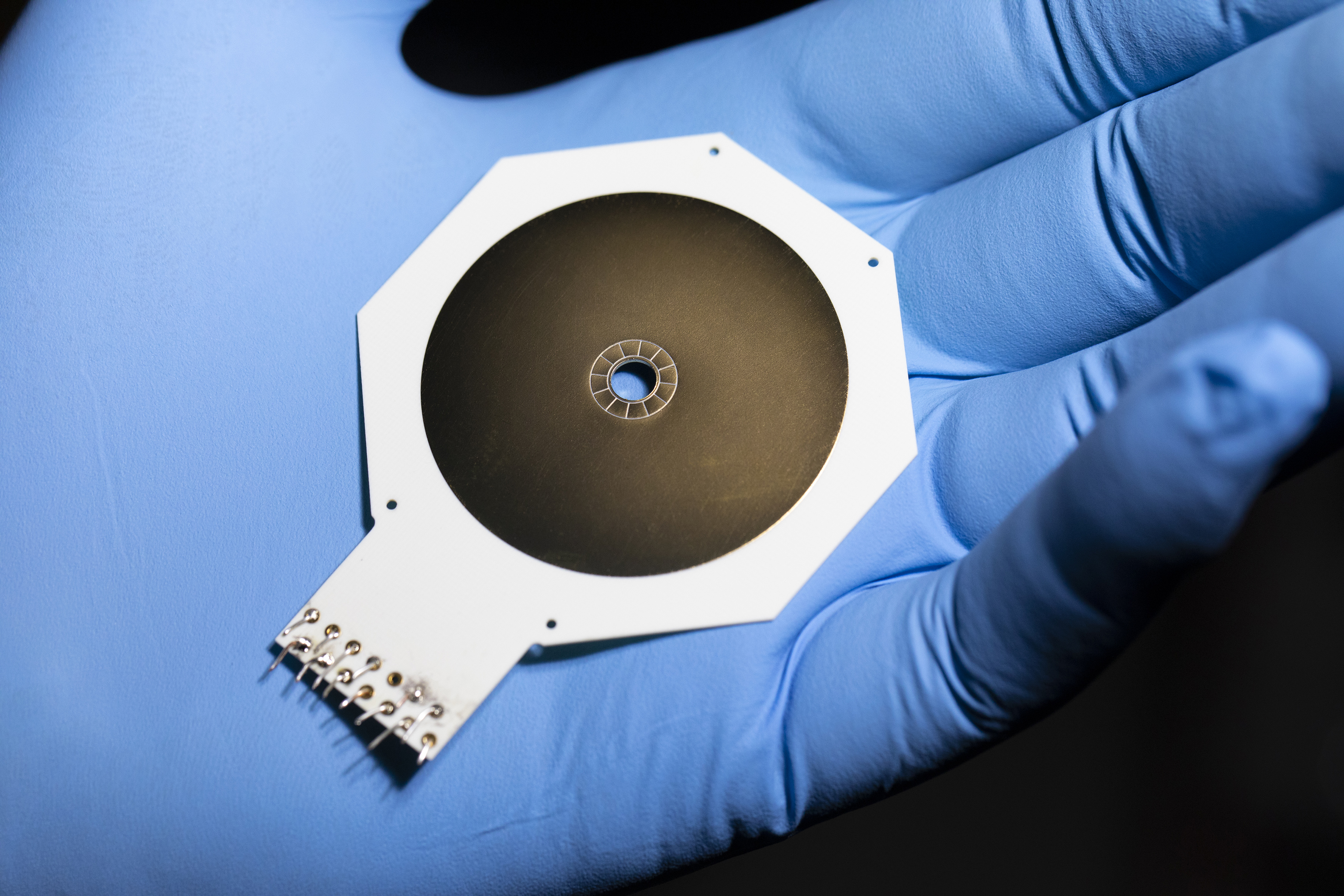
“One of the goals is to run this optimization algorithm with more qubits than has ever been demonstrated before,” Herold said. “On the way, we are also going to show control in a two-dimensional ion crystal in a Penning trap that has not been demonstrated before. That may lead to applications similar to QAOA, in which we can also add more degrees of freedom to analog simulations of quantum systems with trapped ions.”
In the Penning trap, the ions in the crystal will affect one another, allowing interactions to be created throughout the system.
“In choosing an optimization problem that was most natural for trapped ions, we looked at the fact that a collection of ions in a crystal all ‘feel’ one another,” Herold said. “There is a repulsion between them because they are all positively charged, and that leads to a pairwise interaction between each of the particles that can be created in a global way.”
Addressing the Technical Challenges Ahead
Quantum systems tend to be noisy, which can create a significant error rate. The research team includes scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, who are using a supercomputer there to map the best pathway to minimizing noise in the quantum system as it is scaled up.
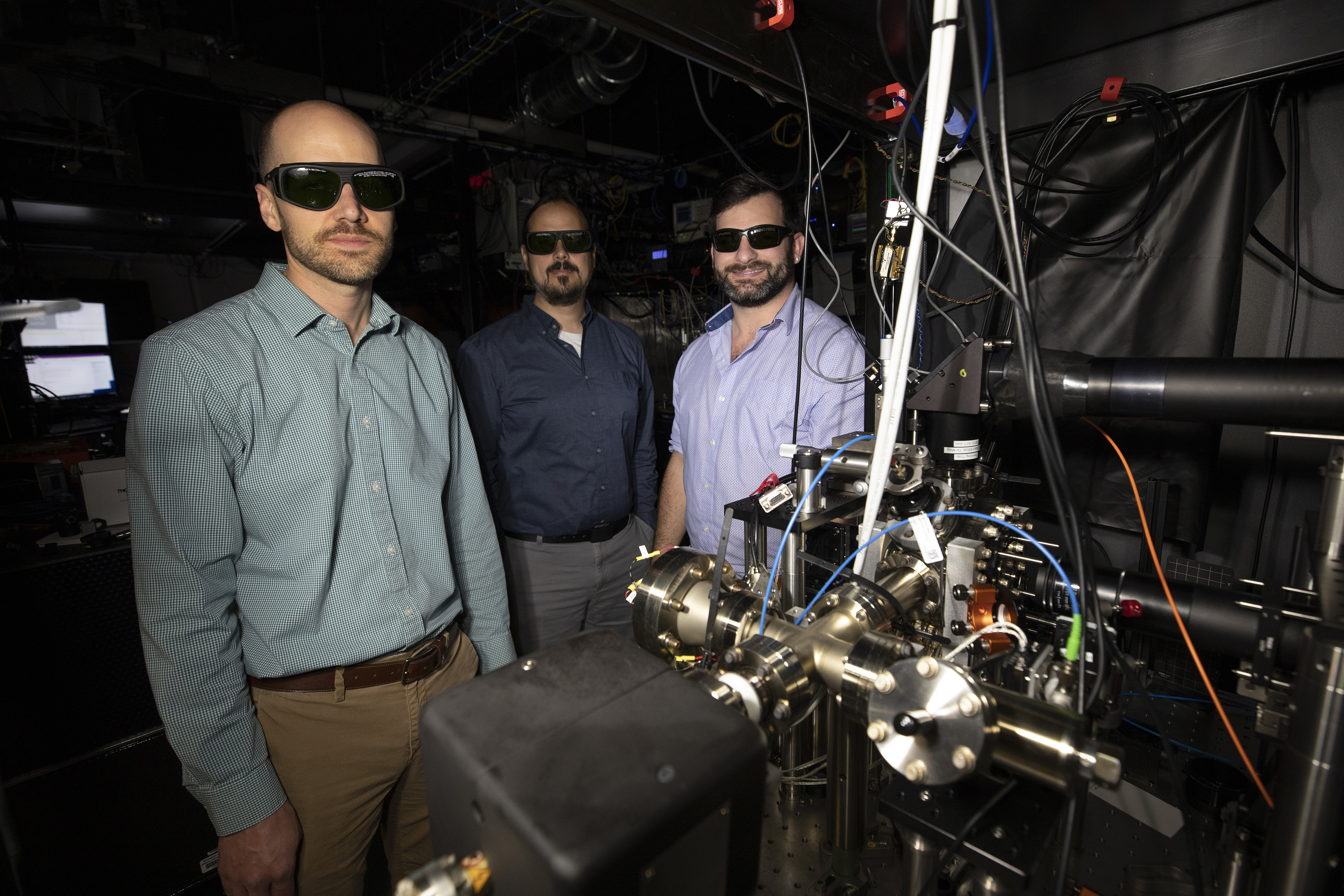
Among the technical challenges ahead will be maintaining a uniform magnetic field using permanent magnets instead of superconducting magnets, which are normally the size of a residential hot water heater.
“We had the idea to make a small trap to get rid of the superconducting magnet,” said Sawyer. “But you have to play tricks to make sure the field is as uniform as possible because you want every ion spinning at the same rate regardless of where it is in the trap. That is tricky to do with small permanent magnets.”
2D Ion Crystal Formed by Doppler-Laser Cooling
The researchers plan to use Doppler-laser cooling – slowing the motion of the ions – to create a crystalline structure in which the calcium ions are arranged in triangular arrays. Creating that stable structure is crucial to the ability to know the location of each ion so that their states can be individually flipped.
“To run this algorithm, we need to be able to point to one ion and then another ion and know exactly where they are at all times to program the particular graphs we need to solve Max-Cut,” said Herold.
Beyond demonstrating a quantum Max-Cut solver, the research could have implications for other optimization problems that are now considered especially difficult because their solution requires many qubits and a complex circuit.
“These optimization problems can often be translated into others, so if you can solve one of them really well, there’s a class of universal problems that can be addressed,” said Herold. “Solving one particular problem can provide the kernel for an optimizer.”
This research is supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) under contract No. HR001120C0046. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing official policies, either expressed or implied, of DARPA or the U.S. government.
Writer: John Toon (John.Toon@gtri.gatech.edu)
GTRI Communications
Georgia Tech Research Institute
Atlanta, Georgia USA
The Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) is the nonprofit, applied research division of the Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech). Founded in 1934 as the Engineering Experiment Station, GTRI has grown to more than 2,800 employees, supporting eight laboratories in over 20 locations around the country and performing more than $700 million of problem-solving research annually for government and industry. GTRI's renowned researchers combine science, engineering, economics, policy, and technical expertise to solve complex problems for the U.S. federal government, state, and industry.
Learn more at www.gtri.gatech.edu and follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.