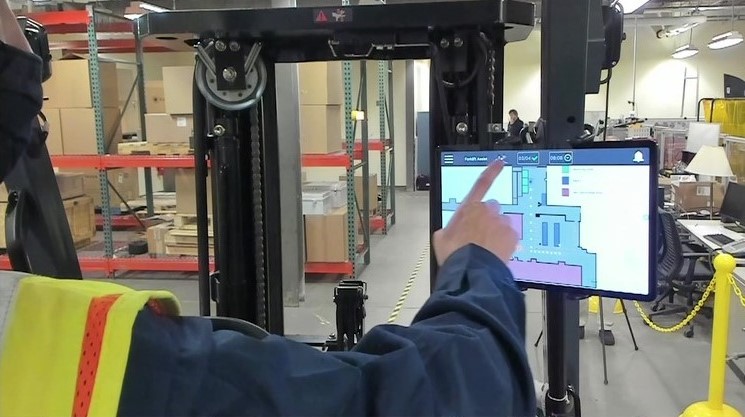
Although warehouses are vital to the success of many organizations, they can also be dangerous to workers and inefficient.
The Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) is working to solve this challenge by integrating its Real-time Intelligent Fusion Service (RIFS) into its Forklift Assist System (FAS) for warehouse operations to streamline efficiencies and enhance worker safety. RIFS, which is a part of FAS, was built with the cross-platform game engine Unity and produces spatial information about a room and then displays that information as meshes on a device, such as a desktop computer or tablet. FAS also includes a camera system that has additional forklift assistance features.
This project has been supported by the U.S. Marine Corps and U.S. Navy, and has also been tested at the Marine Corps Logistics Base in Albany, Georgia.
According to recent estimates, the average U.S. warehouse wastes 6.9 weeks a year on unnecessary motion, which costs the industry $4.3 billion, or 265 million hours of labor annually. Additionally, in 2020, the latest year for which statistics are available, there were 5.5 injury and illness cases per 100 full-time workers and 21 fatalities in the warehouse and storage industry.
RIFS would be incorporated into a warehouse's order management system and provide real-time information about everything going on in the warehouse. For example, a forklift operator could display RIFS on their tablet device and it would help them navigate to their pick up and drop off locations while ensuring they steer clear of obstacles.
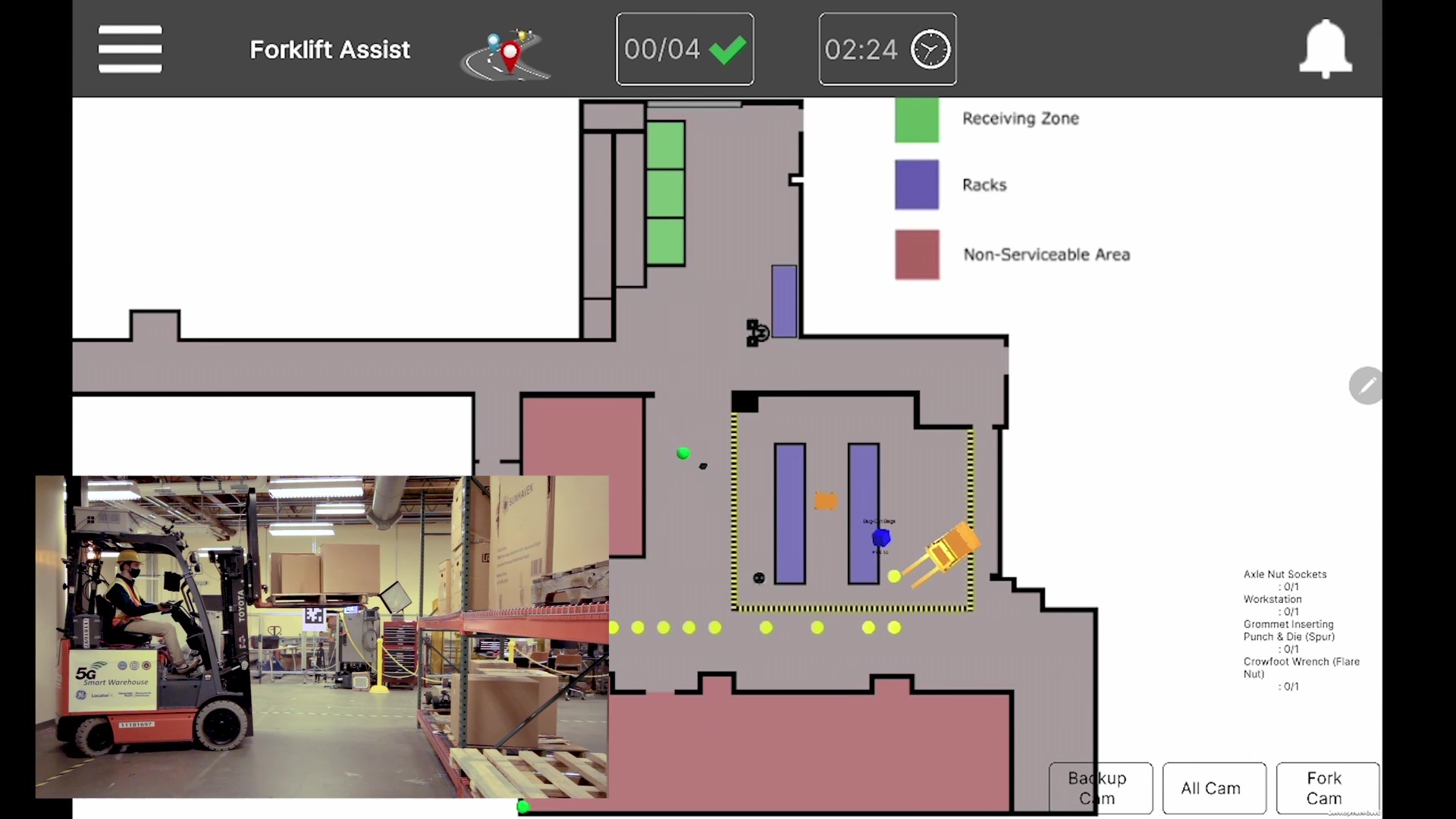
"The system would know where all the other forklifts and people are in the warehouse and have route planning functionality," said Stephen Balakirsky, a GTRI principal research scientist who is leading the project. "A lot of warehouses have one-way aisles and it can be difficult for humans to determine the most efficient path to take, but RIFS could automatically determine that for you."
RIFS works by creating a grid of a particular environment with individual grid spaces that indicate which areas are traversable or not, explained GTRI Research Scientist Emily Strube, who has expertise with RIFS. The software then utilizes a pathfinding algorithm to determine the effort or "cost" required to move from one grid space to another and maps out the most efficient path possible. People and objects are shown as meshes, or geometric objects, in RIFS.
For example, in a warehouse, the algorithm would determine how much effort is required for a worker to move from their current position to their pick up or drop off point and outlines the most expedient route, Strube said.
She added that the algorithm can be adjusted to accommodate changes in a warehouse's workflow and forklift routes.
FAS' camera system would help forklift drivers move towards a pallet and secure it without damaging the warehouse's infrastructure or other pallets and items. The camera system would also have a backup feature to give drivers additional awareness as they move throughout the space in reverse.
To reduce the risk of forklift loads colliding with the top of doorframes, GTRI is also considering developing and installing sensors near doorways to alert drivers of imminent collisions.
"There are lots of different safety features that could be added to this project," Balakirsky said.
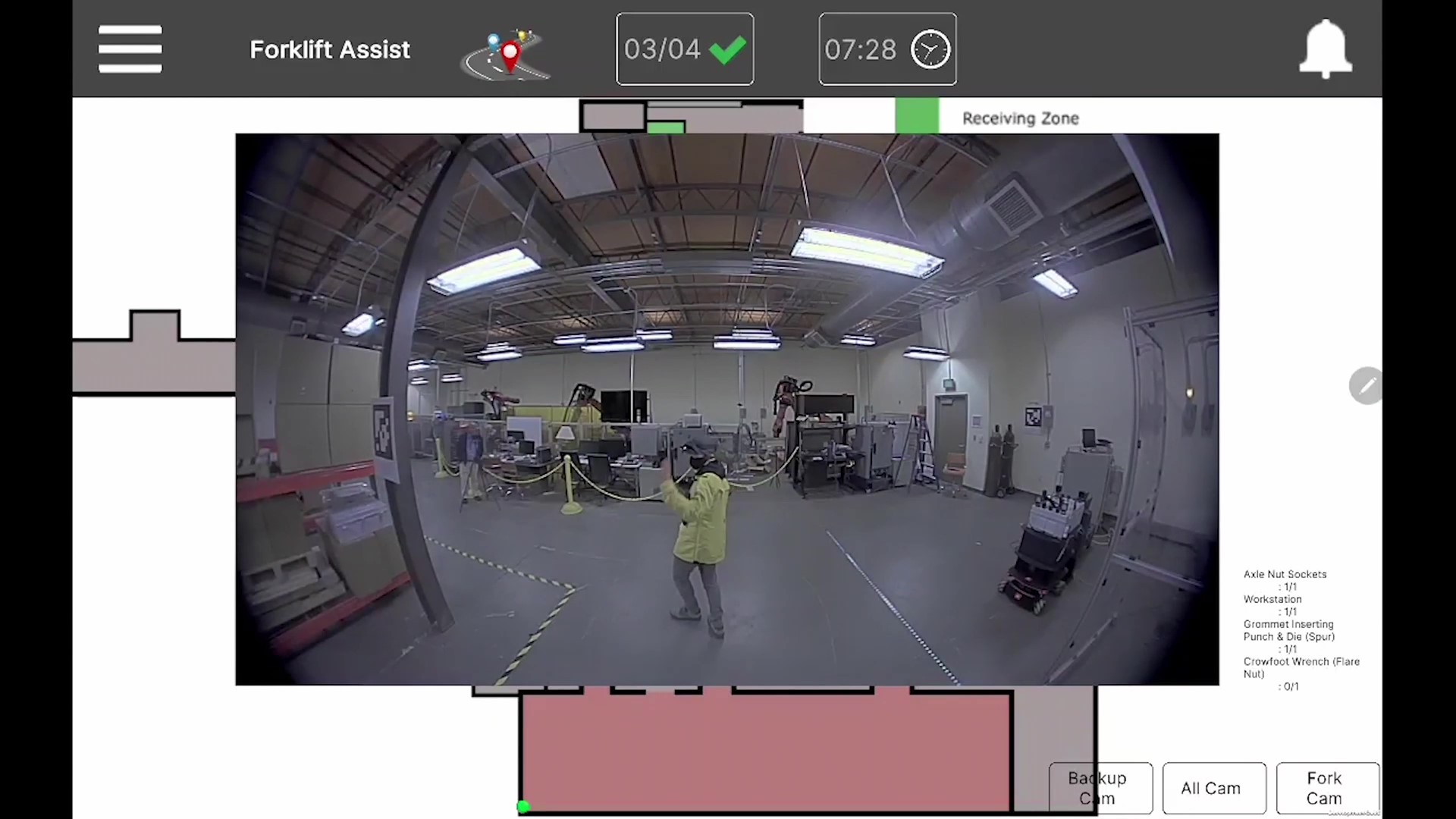
Additionally, GTRI seeks to further utilize RIFS to provide remote inspection and validation of inventory through virtual reality (VR) technology, where the warehouse maps and images would be created by autonomous robots.
RIFS has been incorporated into several other projects, including GTRI's Independent Research and Development (IRAD) of the Year winner for fiscal year 2022, which Strube leads. That project seeks to increase the situational awareness of troops on the ground.
Writer: Anna Akins (anna.akins@gtri.gatech.edu)
Photo Credit: Stephen Balakirsky, Emily Strube
GTRI Communications
Georgia Tech Research Institute
Atlanta, Georgia USA
MORE 2022 ANNUAL REPORT STORIES
MORE GTRI NEWS STORIES
The Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) is the nonprofit, applied research division of the Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech). Founded in 1934 as the Engineering Experiment Station, GTRI has grown to more than 2,800 employees supporting eight laboratories in over 20 locations around the country and performing more than $700 million of problem-solving research annually for government and industry. GTRI's renowned researchers combine science, engineering, economics, policy, and technical expertise to solve complex problems for the U.S. federal government, state, and industry.